Do you want BuboFlash to help you learning these things? Or do you want to add or correct something? Click here to log in or create user.
Subject 2. Total, Average, and Marginal Revenue
#cfa #cfa-level #economics #has-images #microeconomics #reading-15-demand-and-supply-analysis-the-firm
Revenue is the income generated from the sale of output in product markets.
- Total revenue (TR) is the sum of individual units sold multiplied by their respective prices:
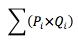
- Average revenue (AR) =
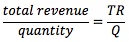
- Marginal revenue (MR) is the change in revenue from selling one extra unit of output:
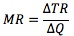
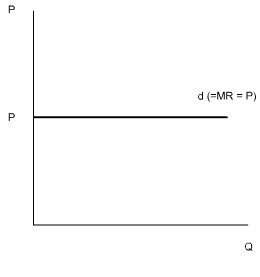
In a perfectly competitive market, each firm is a price taker. Since each unit of output sold by a price taker is sold at the market price, the MR for each unit is also equal to the market price, i.e., P = MR.

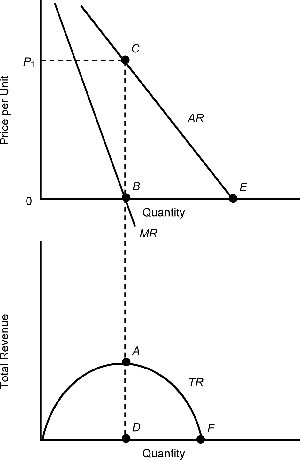
Under imperfect competition, a firm's marginal revenue is always less than the price of its good. Why? As the firm reduces price in order to expand output and sales, there will be two conflicting influences on total revenue.
- The increase in sales due to the lower price will, by itself, add to the revenue of the monopoly.
- The price reduction, however, also applies to units that would otherwise have been sold at a higher price. This factor itself will cause a reduction in total revenue.
These two conflicting forces will result in marginal revenue - the change in total revenue - that is less than the sales price of the additional units. Thus, the marginal revenue curve of the firm will always lie below the firm's demand curve, which is also the market's demand curve.

TR is maximized when MR = 0.
If you want to change selection, open original toplevel document below and click on "Move attachment"
Summary
| status | not read | reprioritisations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| last reprioritisation on | suggested re-reading day | |||
| started reading on | finished reading on |
Details
Discussion
Do you want to join discussion? Click here to log in or create user.